Solar Panel Installation Costs: What Homeowners Need to Know
Introduction
As concerns about climate change and energy costs continue to rise, more homeowners are considering solar panel installation as a viable solution. Solar energy not only provides a sustainable source of power but can also lead to significant savings on utility bills. However, the installation costs of solar panels can be a major consideration for many homeowners. In this article, we will explore the various factors that influence solar panel installation costs, the types of solar systems available, available incentives, potential savings, and what homeowners need to know before making the switch to solar energy.
Understanding Solar Panel Installation Costs
When it comes to solar panel installation, costs can vary widely based on several factors. On average, homeowners can expect to pay between $15,000 and $25,000 for a residential solar panel system before any incentives or rebates. This price range typically includes the cost of equipment, labor, and installation. However, understanding the components that contribute to these costs is essential for homeowners looking to invest in solar energy.
Factors Affecting Solar Panel Installation Costs
Several key factors influence the overall cost of solar panel installation:
Types of Solar Panel Systems
Homeowners have several options when it comes to choosing a solar panel system. Understanding these options can help in estimating costs:
Financing Options for Solar Panel Installation
Financing is a crucial aspect of managing solar panel installation costs. Homeowners have several options to consider:
Incentives and Tax Credits
One of the most significant factors that can reduce the overall cost of solar panel installation is the availability of incentives and tax credits. Homeowners in the United States can take advantage of the Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC), which allows them to deduct a percentage of the cost of solar systems from their federal taxes. As of 2023, the ITC offers a 30% tax credit for solar panel installations.
In addition to the federal tax credit, many states, local governments, and utility companies offer additional incentives, rebates, and performance-based payments. These incentives can significantly reduce the upfront costs of installation and improve the return on investment (ROI) for homeowners. It is essential for homeowners to research and understand the incentives available in their area to maximize savings.
Estimating Long-Term Savings
While the initial costs of solar panel installation can be substantial, homeowners should also consider potential long-term savings. By generating their own electricity, homeowners can significantly reduce or even eliminate their monthly utility bills. The actual savings will depend on several factors, including:
Return on Investment (ROI) for Solar Panels
Calculating the return on investment (ROI) for solar panels involves analyzing installation costs, savings on utility bills, incentives, and the lifespan of the solar system. On average, homeowners can expect to see a payback period of 5 to 10 years, depending on local energy costs, system size, and available incentives. After the payback period, homeowners can enjoy several years of free electricity, making solar a financially sound investment in the long run.
Common Misconceptions About Solar Panel Costs
Despite the growing popularity of solar energy, several misconceptions about solar panel installation costs persist:
Choosing the Right Solar Installation Company
Selecting a reputable solar installation company is crucial for ensuring a successful installation and maximizing the benefits of solar energy. Homeowners should consider the following factors when choosing a solar provider:
Conclusion
Solar panel installation can be a significant investment for homeowners, but understanding the costs, incentives, and potential savings can help make the decision more manageable. By considering factors such as system size, type of solar panels, financing options, and choosing a reputable installation company, homeowners can optimize their solar investment. As solar technology continues to advance and more incentives become available, the future of solar energy looks brighter than ever. By investing in solar, homeowners not only reduce their reliance on fossil fuels but also contribute to a more sustainable future for generations to come.
Explore

Find the Best Nearby Solar Panel Installers: Your Complete Guide to Local Solar Solutions
Everything You Need to Know About Window Replacement: Costs, Options, and Top Installers

Car Insurance: What You Need to Know and How to Choose the Right Coverage
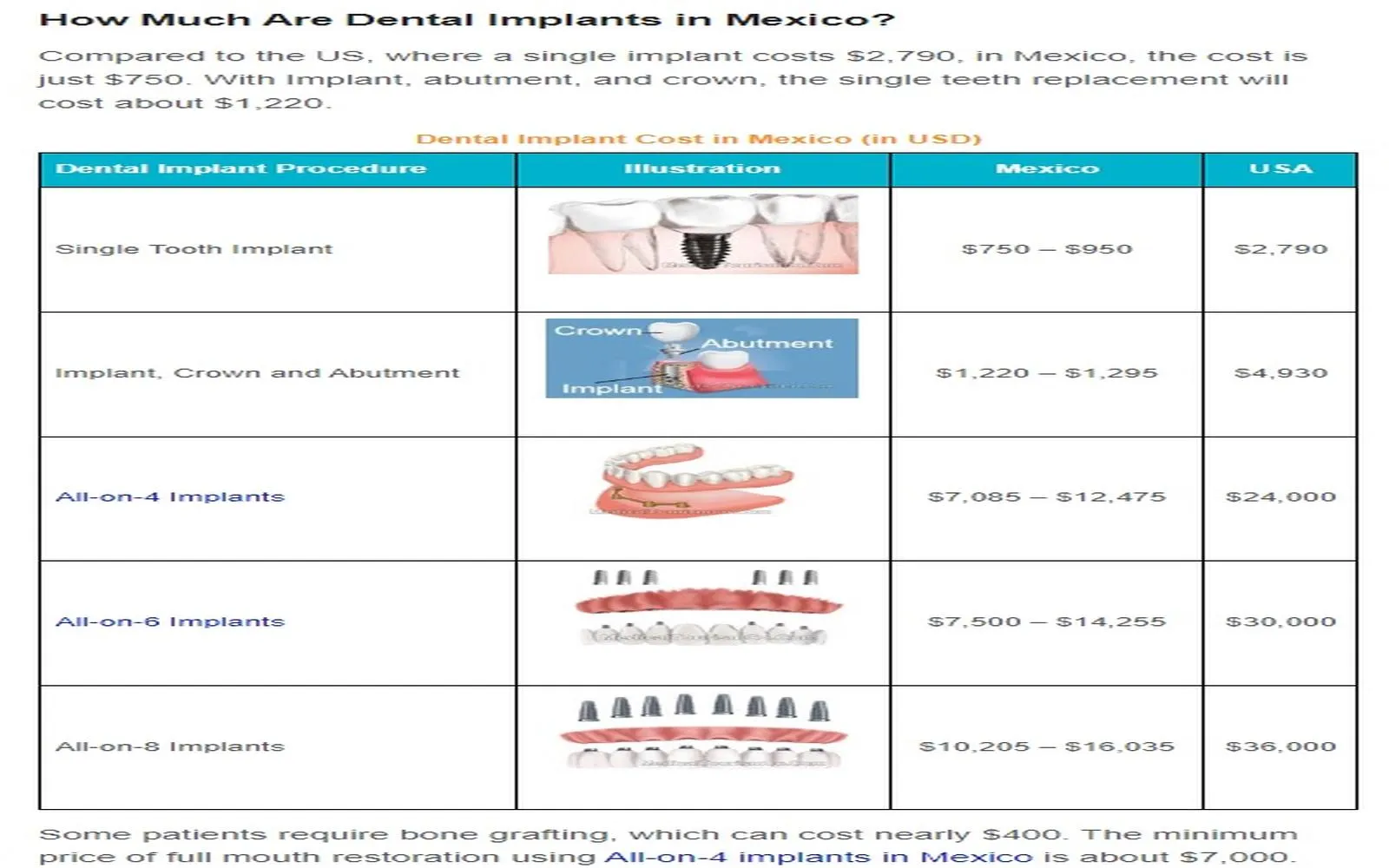
Comprehensive Guide to Dental Insurance with Implant Coverage: What You Need to Know

Private Health Insurance: Compare Plans, Costs & Benefits
Bright Savings: Your Guide to Affordable Solar Panels for Every Home

Find Top Solar Companies Near You for Home Energy Solutions

The Future of Solar Roofing: Harnessing the Power of the Sun for Your Home
