Strengthen Your Cloud Security: Best Practices & Strategies
Introduction
In today's digital age, cloud computing has become a cornerstone of business operations. As organizations increasingly migrate their data and applications to the cloud, the need for robust cloud security has never been more critical. Cyber threats are evolving rapidly, making it essential for companies to adopt best practices and strategies to protect their cloud environments. This article explores effective methods to strengthen your cloud security, ensuring that your data remains safe from unauthorized access and breaches.
Understanding Cloud Security
Cloud security refers to a set of policies, technologies, and controls deployed to protect data, applications, and infrastructure associated with cloud computing. Unlike traditional on-premises security, cloud security requires a shared responsibility model, where both the cloud service provider (CSP) and the customer play roles in securing cloud resources. Understanding this model is crucial for implementing effective security measures.
Key Threats to Cloud Security
Before delving into best practices, it's vital to understand the common threats that can compromise cloud security:
Best Practices for Cloud Security
Implementing best practices is essential to strengthen cloud security. Here are some strategies that organizations should consider:
1. Choose a Reliable Cloud Service Provider
Before migrating to the cloud, it’s crucial to select a reputable CSP that prioritizes security. Look for providers that comply with industry standards and regulations, such as ISO 27001, GDPR, and HIPAA. Ensure they offer robust security measures, including data encryption, access controls, and regular security audits.
2. Implement Strong Access Controls
Access control is a fundamental aspect of cloud security. Organizations should implement the principle of least privilege (PoLP), granting users the minimum level of access necessary to perform their duties. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) should also be employed to add an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple methods.
3. Encrypt Data at Rest and in Transit
Data encryption is a key component of cloud security. Encrypting sensitive data both at rest and in transit ensures that even if attackers gain access to the data, they cannot read it without the encryption keys. Organizations should choose strong encryption standards, such as AES-256, and manage encryption keys securely.
4. Regularly Update and Patch Systems
Keeping cloud systems up-to-date is critical for mitigating vulnerabilities. Organizations should establish a routine for applying updates and patches for all software and applications, including those provided by the CSP. This proactive approach helps close security gaps and protects against known threats.
5. Conduct Regular Security Audits
Regular security audits help identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with security policies. Organizations should conduct comprehensive assessments of their cloud environments, including configuration reviews, vulnerability scans, and penetration testing. These audits can uncover weaknesses that need to be addressed promptly.
6. Monitor and Log Activities
Continuous monitoring of cloud environments is essential for detecting suspicious activities. Organizations should implement logging mechanisms to track user activities, access attempts, and system changes. Advanced security information and event management (SIEM) tools can analyze logs in real-time, helping organizations respond quickly to potential security incidents.
7. Develop an Incident Response Plan
An effective incident response plan is critical for minimizing damage in the event of a security breach. Organizations should outline procedures for identifying, responding to, and recovering from security incidents. Regularly testing and updating the incident response plan ensures that teams are prepared to act swiftly when a breach occurs.
8. Educate Employees on Security Awareness
Employees are often the weakest link in security. Conducting regular security awareness training helps employees recognize potential threats, such as phishing attacks and social engineering. Educated employees are better equipped to identify suspicious activities and follow security protocols, reducing the risk of human error.
9. Configure Security Settings Properly
Many cloud services come with default security settings that may not be sufficient for your organization’s needs. Take the time to review and customize security configurations based on your specific requirements. This includes setting up firewalls, enabling logging features, and configuring network segmentation to limit exposure.
10. Use Cloud Security Tools and Solutions
Various cloud security tools and solutions can enhance the security posture of your cloud environment. Consider utilizing cloud access security brokers (CASBs), data loss prevention (DLP) solutions, and identity and access management (IAM) tools. These technologies can provide additional layers of security, automate compliance, and offer visibility into cloud usage.
Strategies for Cloud Security Compliance
Compliance with industry standards and regulations is essential for maintaining cloud security. Organizations should implement the following strategies to ensure compliance:
1. Understand Regulatory Requirements
Different industries are subject to various regulations regarding data protection and privacy. Organizations must understand the specific requirements that apply to their industry, such as GDPR for businesses operating in Europe or HIPAA for healthcare organizations in the U.S. This knowledge helps guide security measures and compliance efforts.
2. Implement Data Classification and Governance
Data classification involves categorizing data based on its sensitivity and importance. Organizations should establish data governance policies that define how sensitive data is handled, stored, and accessed. This ensures that appropriate security measures are applied based on the classification of the data.
3. Regularly Review and Update Policies
Security policies should be living documents that evolve as the organization and threat landscape change. Regularly review and update security policies to reflect new regulations, emerging threats, and changes in cloud architecture. This ensures that your organization remains compliant and adequately protected.
4. Collaborate with Cloud Service Providers
Collaboration with your CSP is essential for maintaining compliance. Ensure that your provider understands your compliance requirements and can demonstrate how their services support them. Request regular reports on security measures, compliance certifications, and audit results to stay informed about your cloud environment's security posture.
Future Trends in Cloud Security
As cloud computing continues to evolve, so too will the strategies and technologies used to secure it. Here are some emerging trends to watch for in cloud security:
1. Zero Trust Security Model
The zero trust security model operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify." This approach requires continuous authentication and validation of users and devices, regardless of their location. As organizations adopt this model, cloud security will become more resilient to insider threats and compromised credentials.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning technologies are increasingly being integrated into cloud security solutions. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies, helping to detect potential security threats in real-time. As AI-driven security solutions become more sophisticated, they will play a crucial role in enhancing cloud security.
3. Increased Regulation and Compliance Requirements
As data breaches continue to rise, regulatory bodies are likely to implement stricter compliance requirements. Organizations must stay informed about evolving regulations and adapt their security strategies accordingly to avoid penalties and protect sensitive data.
4. Cloud-Native Security Solutions
Cloud-native security solutions are designed to protect cloud environments specifically. These solutions leverage microservices, containers, and serverless architectures to provide security at every layer of the cloud stack. As organizations adopt cloud-native technologies, the demand for tailored security solutions will grow.
Conclusion
Strengthening cloud security is an ongoing process that requires a proactive approach. By implementing best practices and strategies outlined in this article, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of data breaches and cyber threats. As the cloud landscape continues to evolve, staying informed about emerging trends and adapting security measures accordingly will be crucial for maintaining a secure cloud environment. Ultimately, a robust cloud security strategy not only protects sensitive data but also fosters trust with customers and stakeholders, empowering organizations to thrive in the digital age.
Explore

Cloud Web Security: Protecting Your Cloud Infrastructure

Data Security Management: Essential Strategies for Protection

Affordable Cloud Security: Protect Your Data Without Breaking the Bank
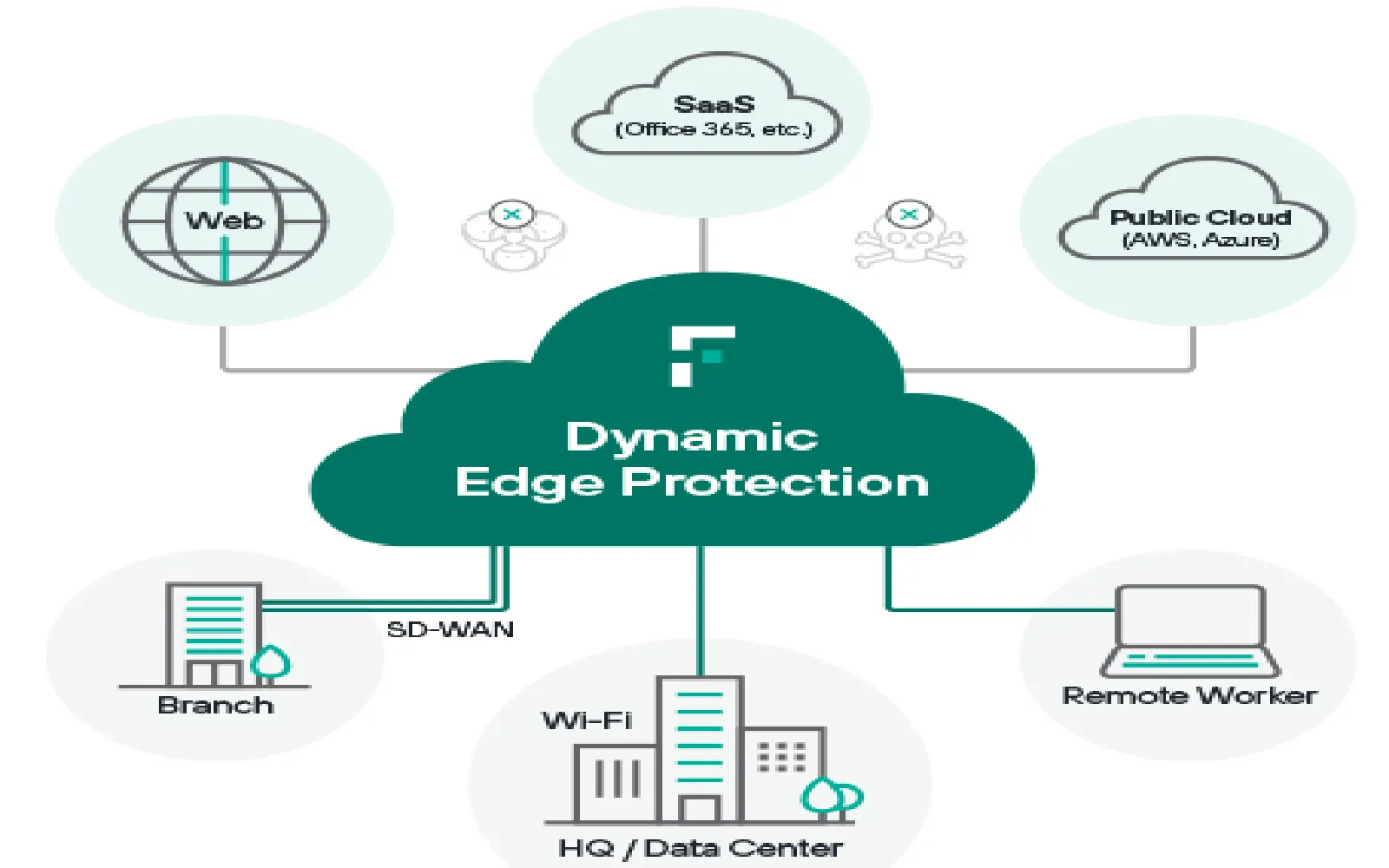
Top Cloud Security Providers: Protecting Your Business Online

Best Cloud Security Services to Protect Your Business Data
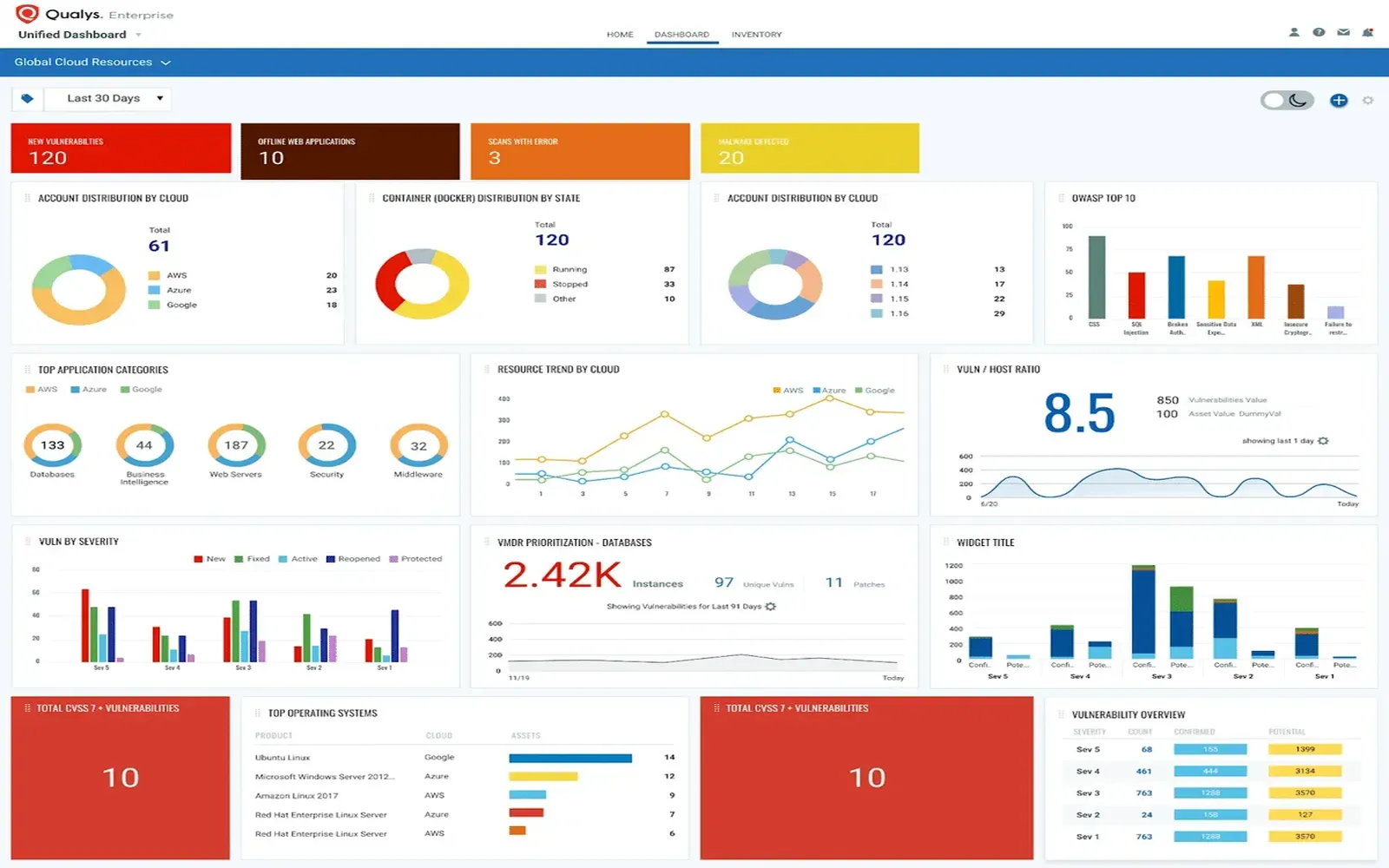
Top Cloud Security Providers: Safeguarding Your Data in the Digital Age
Cloud Services in Daily Life: How the Cloud is Changing the Way We Live

Unlock Your YouTube Potential: Proven Strategies to Skyrocket Your Video Views!
